What is Microservices?
Microservices is an architectural style where a large application is broken down into smaller, independent services that communicate with each other through APIs. Each microservice is responsible for a specific function and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This approach allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and ease of maintenance.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It helps you to manage containerized applications in a clustered environment.
URL Routing
Navigating between services can be challenging as each one operates on its own unique ports. For example products in http://localhost:8980 and orders in http://localhost:8981
Kubernetes is a powerful tool for managing microservices, and one way to use it is by creating Services to handle specific URL paths.
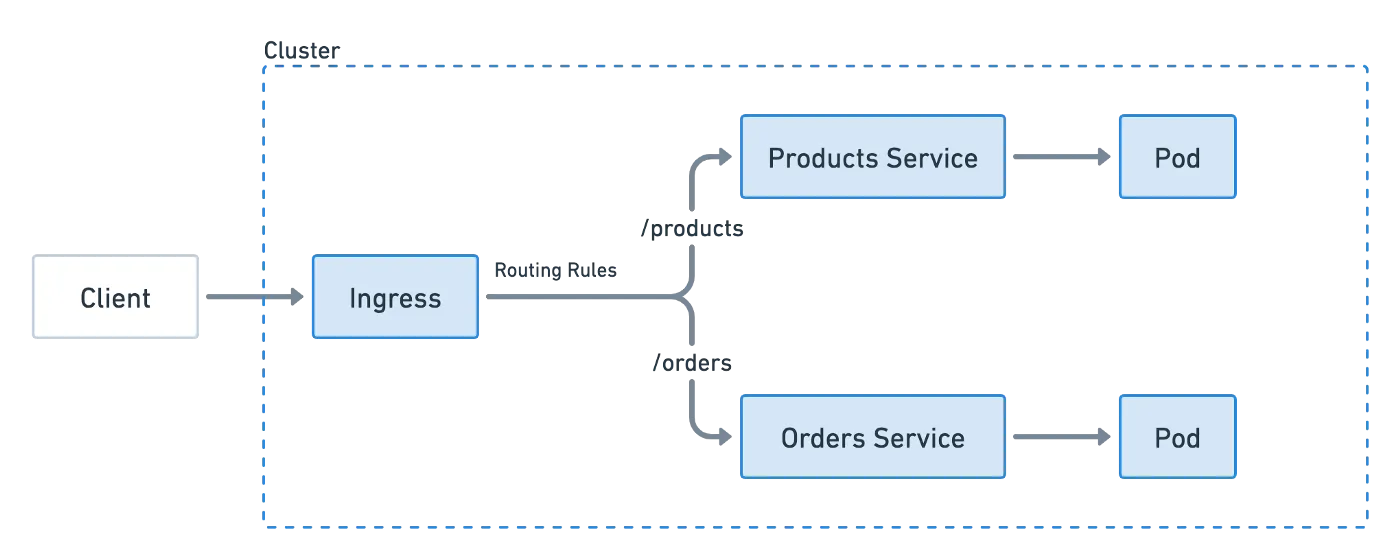
In this blog post, we will show you how to navigate between services using URL paths http://localhost/products and http://localhost/orders using Ingress.
First, let’s create a service for the /products path. Here is an example YAML file that you can use:

# products-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: products-svc
spec:
selector:
app: products
ports:
- port: 8980
name: products-svc-port
protocol: TCP
targetPort: products-port
This YAML file creates a service named products-svc that selects pods with the label app: products. It also defines a port named http that listens on port 80 and forwards traffic to port 8980 on the selected pods.
Next, let’s create a service for the /orders path. Here is an example YAML file that you can use:

# orders-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: orders-svc
spec:
selector:
app: orders
ports:
- port: 8981
name: orders-svc-port
protocol: TCP
targetPort: orders-port
This YAML file creates a service named orders-svc that selects pods with the label app: orders. It also defines a port named http that listens on port 80 and forwards traffic to port 8981 on the selected pods.
You can create these services by running the following command:
kubectl apply -f products-svc.yaml
kubectl apply -f orders-svc.yaml
Once you’ve created these Services, you can use them to route traffic to the appropriate pods based on the URL path. For example, requests to /products will be handled by the products-svc Service, while requests to /orders will be handled by the orders-svc Service.
It’s worth noting that this is just a basic example, and in real world scenarios, you would probably want to use an Ingress or a LoadBalancer to handle routing requests to multiple services.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: microservices
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
labels:
name: microservices
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: /products
backend:
service:
name: products-svc
port:
number: 8980
- pathType: Prefix
path: /orders
backend:
service:
name: orders-svc
port:
number: 8981
Reference GitHub link: https://github.com/sentinelfoxinc/k8s_ingress_http_rules




